How the Russian Federation circumvents sanctions for the production of high-tech weapons?

The full-scale phase of the Russian-Ukrainian war continues. During this time, the Russian Federation became a world leader among countries subject to international sanctions. However, the loopholes that allow the Russian Federation to bypass them remain and exist. Civilian technology is quickly adapting to the military needs of a terrorist state, and the long process of improving sanctions and restrictions is obviously not keeping up with these changes.
For example, metalworking machines with numerical program control (CNC machines, hereinafter – сomputer numerical control machines) are necessary for high-precision milling and are currently the most demanded "civilian" equipment used by the Russian Federation for military purposes. Of course, most of this equipment is produced outside the Russian Federation and, unfortunately, despite the sanctions, Russians are actively buying it.
Russia uses any type of machine tool with the computer numerical control (CNC) in the production of weapons. This is evidenced by dozens of videos from their military factories, which literally work in three shifts.
The geography of the supply of high-tech metalworking machines is impressive in its diversity. These are units manufactured in Japan, Germany, the USA, Switzerland, South Korea, Italy, the Czech Republic and other countries. Of course, trade with these countries is somewhat more difficult, although not impossible, but you can always try to buy something similar in China.
We also do not forget that the corresponding machines are also produced in Taiwan, from where they can also be purchased through third countries. However, it is important to note that in the manufacture of these machines in China and Taiwan, parts produced in G7 countries and the modules of the computer numerical control machines (CNC) from Germany or Japan are used. And so far, only Japan has completely banned the export of machines with the computer numerical control (CNC) to Russia. This happened in April 2023.
Other G7 countries limited themselves to strengthening export controls. But such actions, as we can see, are not enough.
Russia began to import these units through other countries – China, Turkey, UAE, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan. The Russians call their smuggling "parallel imports".
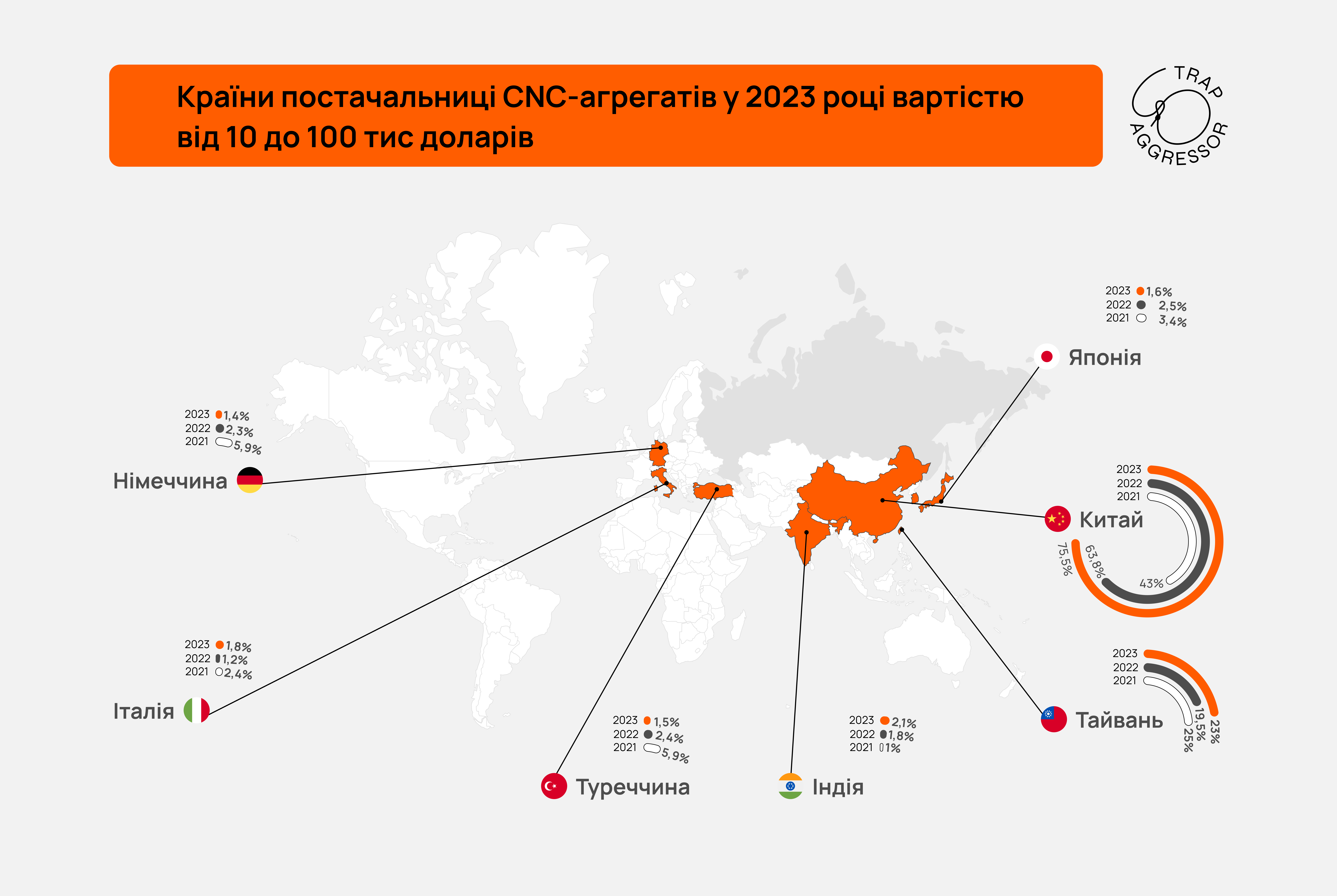
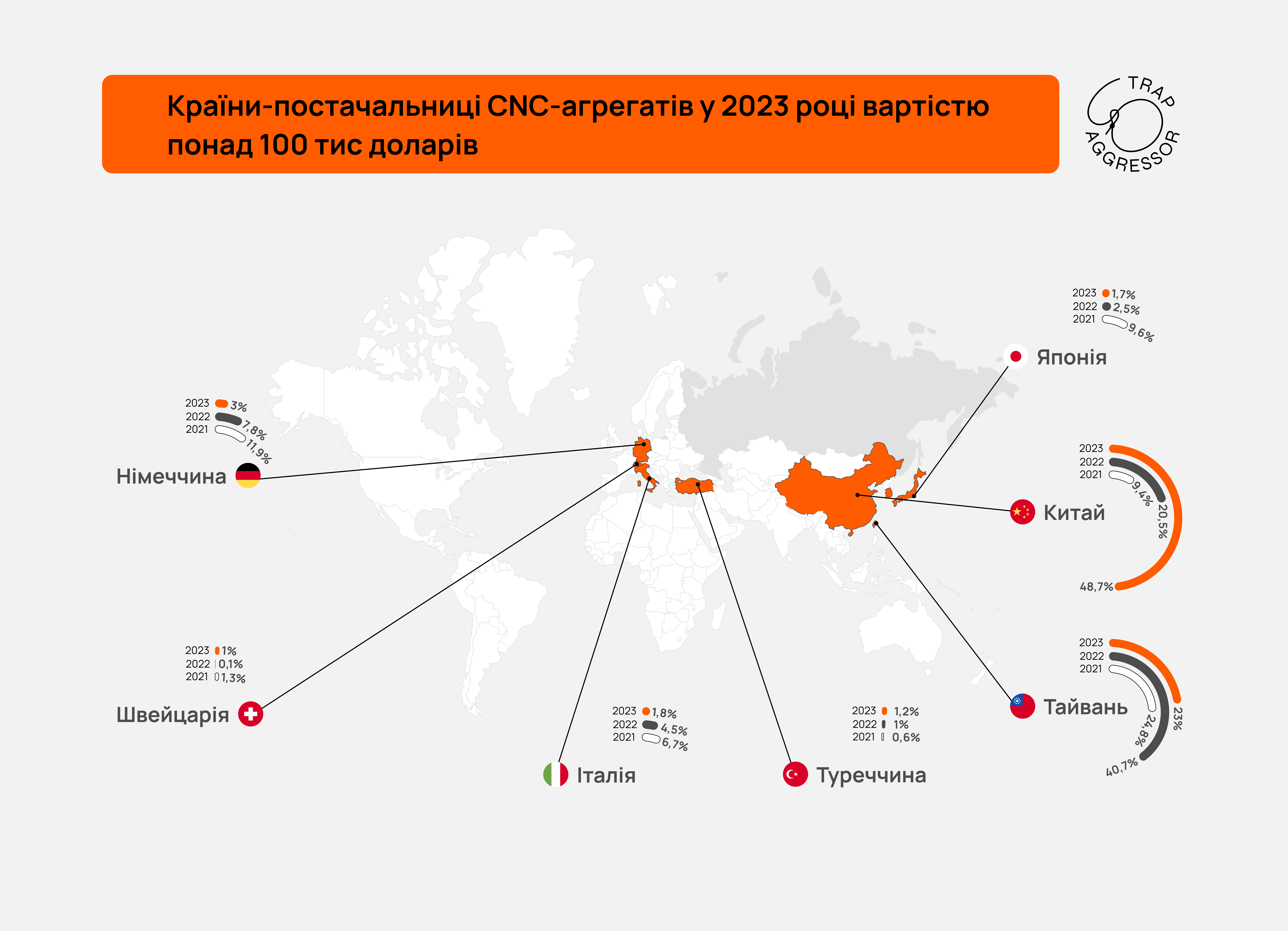
As part of the Trap Aggressor project, we investigated the geography and volumes of "parallel" deliveries of the computer numerical control machines (CNC). Among the countries – suppliers of aggregates worth more than 100 thousand dollars in 2023. In the USA we find China, Taiwan, South Korea, Germany, Japan, Switzerland, Turkey, Italy.
China, Taiwan, South Korea, India, Germany, Turkey, Japan, and Italy are among the countries that supply aggregates worth more than ten thousand dollars.
In other words, Russia is re-equipping with Chinese equipment and significantly increasing the consumption of the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools. And at the international level, something needs to be done about it. Sanctions and restrictions are not working perfectly.
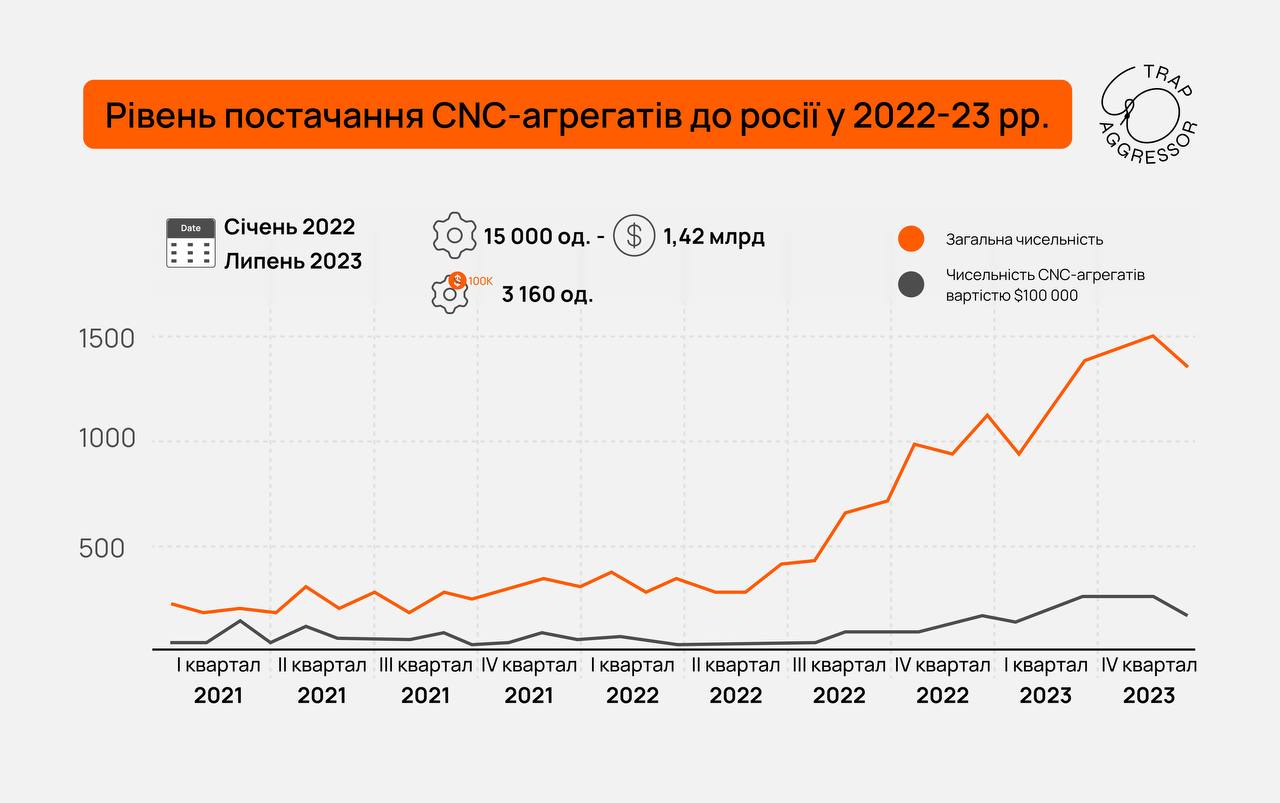
From January 2021 to July 2023, Russia imported more than 15,000 the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools with a total value of $1.42 billion. Of these, 3,160 cars cost more than $100,000 per unit.
It is interesting that Russia does not hide at all that it uses machines from the manufacturing companies of the G7 countries for the production of weapons. On the contrary, the Russian Federation is proud of this achievement.
On YouTube, we find dozens of videos from military factories (one, two, three, four, five videos) where foreign equipment is demonstrated. Some videos were filmed even in 2023.
Russian web resources, in particular the database of state contracts, store information about which companies have cooperated with military plants in the Russian Federation. However, such contracts have ceased to be published since 2018, so only previous cooperation and deliveries can be recorded online. However, it is obvious that the cooperation continues to this day.
And finally. Almost all companies in Russia related to the import or production of the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools had experience of cooperation with military factories. Who would believe that in Putin's Russia, any business entity engaged in industrial production can refuse such departments as the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (FSB) or the Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (GRU) to fulfill individual military orders?
During the research by our insiders on the OSINT analytics and data of the Ukrainian special services, additional interesting points were found. Japanese "precision" Tsugami aggregates are imported through China. Okuma aggregates with specified serial numbers are imported with hidden exporter information. In turn, Fanuc products go through Hong Kong, and Kitanura is imported through a Russian hub in Turkey (Akhmedov’s Group). Modules for the computer numerical control machines (CNC) from Fanuc are available for Russian machine manufacturers as part of units from China, Taiwan, and South Korea. These aggregates were presented at the metalworking exhibition in May 2023.
Aggregates from the Hermle, Stadler Keppler, Deckel, DMG Mori manufacturing companies are sent from Germany through Turkey to the Russians.
Products are transported from the Czech Republic by the Inter Style Plus company from Kyrgyzstan, which is the official representative of the world's leading manufacturers of machine tools and components. Cooperation has been established with PHIFFNER, MORI-SAY, FERMAT, KOVOSVIT MAS, TAJMAC-ZPS and other leaders in the field of machine tool technologies.
As you can see, export-import control still leaves much to be desired. Russians still have access to purchase aggregates and parts for them from companies located within the G7 group of countries and other states that allegedly do not support Russian intervention in Ukraine.
How to get out of the vicious circle of supplying the computer numerical control machines (CNC) to Russia?
Major manufacturers of the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools should at least be concerned about being sanctioned in the USA. Because who would believe that manufacturing companies do not know the final "consumers" of the respective products in a world where any counterparty is not far from each other.
Any written request by the USA government to a manufacturer of aggregates regarding cases of imports to Russia may make the supplier wonder: are they not helping to produce high-tech weapons for the war in Ukraine and for supplying exile countries with developed terrorist tendencies?
Moreover, secondary sanctions against dubious importers will help slow down the pace of equipment deliveries to the Russian Federation. Special attention should be paid to manufacturers of the computer numerical control machines (CNC) modules, i.e. such companies as Siemens (Germany), Heidenhain (Germany), Fanuc (Japan).
After all, it's time to launch new control methods for tracking the final "consumer", in particular, for these giant companies.
It is also advisable not to forget about the countries that help Russia with so-called double imports. In the case of importing aggregates to China, Turkey, the UAE, Hong Kong, multiple checks of final counterparties should be a mandatory element of control. At the same time, it is necessary to take additional special measures for Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan – the final consumer must prove that the companies really exist and are not just written on paper. With the provision of photos and videos of the facilities, as well as copies of existing contracts with their customers and other suppliers. Finally, in this perspective, we note that special attention must be paid to the supply of spare parts for high-tech machines.
Special thanks to the OSINT researcher Levko Bidi for sharing the database for the article.
Please select it with the mouse and press Ctrl+Enter or Submit a bug










 Login with Google
Login with Google