How to reduce the effects of war on cultural heritage: how the Ukrainian Armed Forces can help

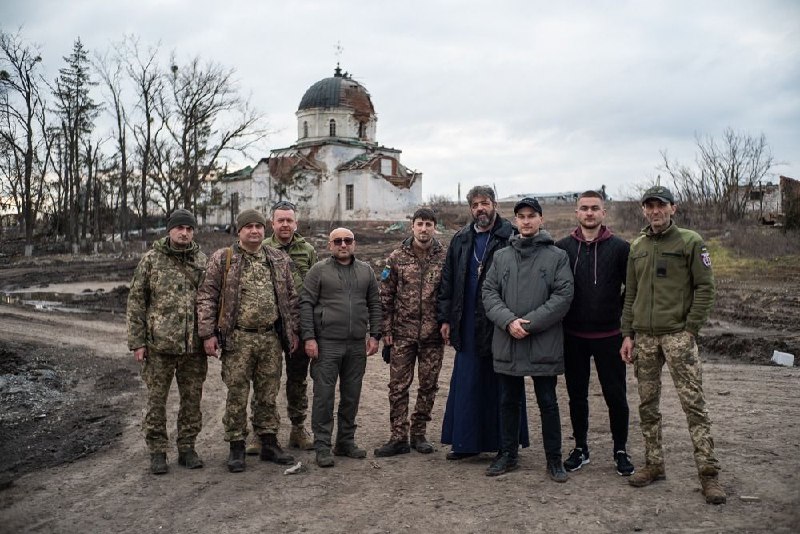
On another frosty morning, members of the working group of the Territorial Defense Forces of the Armed Forces of Ukraine on the implementation of international humanitarian law were documenting the consequences of aggression in the frontline zone. This time it was the territories of Kharkiv region, which had just been liberated from occupation. Moving from one place to another, we looked at the remains of what used to be a village. Instead of houses with farms on both sides of the road, there were only ruins and the remains of destroyed vehicles. According to the business trip plan, we were to explore the church in the village of Komyshuvate, a 19th-century architectural monument.
During the time of the working group's existence, we have seen hundreds of destroyed and war-damaged cultural objects. But every time it evokes emotions. And here, in Komyshuvate, it happened again. The church was not only destroyed. The Russian military dug a pit close to its foundation to shelter a tank, and judging by the remains of belongings and medical supplies, they organized a sort of hospital in it. Such finds are not uncommon in the liberated territories.
Since 2014, and especially since the full-scale invasion, the Russian authorities have stolen, destroyed, and damaged thousands of cultural sites in Ukraine. We understand that these are not sporadic actions, but must be seen as part of a long-term policy. Crimes against Ukrainian culture began not in 2022 or even 2014, but many centuries ago. They began in the Russian Empire and continued during the occupation of Ukraine in the Soviet period, when culture suffered the greatest losses.
We have a clear understanding that the crimes committed after the full-scale invasion are only a small piece of the puzzle of the destruction of Ukrainian culture, which has been going on since the time of the Russian Empire and is an integral part of Russia's policy aimed at destroying Ukrainians as a nation.
The political and military leadership of the aggressor country has repeatedly stated that "denazification" is their strategic goal in this phase of the war. Accordingly, the Commander-in-Chief and the governing bodies of the General Staff of Ukraine should consider the protection of national cultural values and cultural heritage as a strategic task of the Defense Forces.
Ukraine, like other signatory states to the 1954 Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict, is obliged to prepare or create special units (services) or special personnel in its armed forces to ensure respect for cultural property and cooperation with civilian authorities responsible for its protection. After all, the protection of cultural property, according to the Convention, includes the protection and respect for these values.
According to the Ministry of Culture and Information Policy of Ukraine, at least 863 monuments were destroyed or damaged as a result of the full-scale Russian aggression between February 24, 2022, and September 25, 2023, 119 of them of national importance and 674 of local importance. However, this official number does not include archives, museums, libraries, and other objects defined by international law as cultural property. Obviously, the actual number of affected sites is much higher.
However, while in places where the competent authorities have free access, the algorithm of protection actions is more or less clear, what should be done in the so-called areas of responsibility of the military?
To answer this question, it is important to take a look at the experience of other countries where the protection of cultural heritage is one of the tasks of the armed forces and has been implemented in many countries.
The Cultural Property Protection Unit of the British Armed Forces is a separate unit within the Reserve Forces, established in 2017 after the British government officially ratified the 1954 Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict. Its mission is to provide advice to military commanders on the protection of works of art and cultural heritage in combat zones. The unit's personnel are also directly involved in investigating cases of theft of cultural property in the combat zone and in training specialists in the protection of cultural property of partner countries, if necessary.
In the U.S. Armed Forces, the protection of cultural property is the responsibility of the U.S. Army Civil Affairs and Information and Psychological Operations Command. Military service in this military command is mainly performed by representatives of the US Army Reserve, which allows for the involvement of a wide range of specialists in the performance of civil affairs tasks, as the personnel combine military service with a civilian specialty.
The tasks of protecting and preserving cultural property are carried out both during hostilities and during "transitional governance" measures, which involve the actions of the US military command to ensure control and continuity of government functions in the area of responsibility.
At the same time, the protection of cultural property in the concept of NATO member states, in particular the United States and the United Kingdom, is closely linked to the generally accepted concept of protecting the population during military, stabilization, and humanitarian operations, and is an important component in the development of peace and security.
Let's get back to our realities. Given the fact that we are in a state of war on our territories, they are significantly different from those of our partners. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop and implement a Ukrainian model for the protection of cultural property in the context of armed conflict. At the same time, it is important to understand that this is currently a concomitant task for the Armed Forces.
Given the scale of the destruction and the duration of the conflict, in order to involve and operate the Armed Forces of Ukraine in the case of destruction or damage to cultural heritage sites and cultural property in the areas of hostilities, it seems appropriate to create a separate unit (at the company or battalion level) for the protection of cultural heritage and cultural property. However, this is a long process. That is why the working group of the Territorial Defense Forces Command proposed a unique model. According to this model, a department has already been established at the level of the civil-military co-operation of the Territorial Defense Forces to coordinate this work. In addition, the problem of involving civilian specialists who specialize in the study of cultural heritage in this work has been solved. For this purpose, a project of a military unit for the protection of cultural heritage was launched. This is the so-called cultural volunteer formation of the territorial community (VFTC), which has already been joined by cultural professionals who are able to effectively assess the damage, take the priority measures necessary to preserve monuments and values, and organize evacuation. By joining the VFTC, cultural heritage specialists will be able to join trips to the contact line as needed.
In addition, many steps have been taken to ensure respect for cultural heritage and cultural property during the planning and conduct of hostilities. Respect primarily concerns the military's situational awareness of the presence of cultural monuments protected by IHL in the areas of responsibility of units, and taking their presence into account when conducting and planning combat operations. Currently, on the information and communication platform of the Armed Forces of Ukraine Delta, developed and administered by the Center for Innovation and Development of Defense Technologies of the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine, the command of the Territorial Defense Forces of the Armed Forces of Ukraine has created and is filling the information layer "Objects protected by international humanitarian law", which is an electronic map displaying information on more than 60 thousand cultural heritage sites. The Damages layer has also been created, which contains documented information about cultural heritage sites and cultural property destroyed or damaged during the armed conflict (information about almost 400 of them has been added so far). Cultural heritage sites are being actively marked with "blue shields" and entered into the relevant registers to obtain legal status. For example, in December, five more cultural heritage sites in Ukraine were granted enhanced protection.
All of this is important, in part, to ensure that the enemy cannot justify an attack on these facilities by claiming ignorance. The issue of creating a separate information layer for the area affected by the destruction of the Kakhovka HPP is currently being considered. After all, the working group of the Territorial Defense Forces took an active part in the work of the Interagency coordination center for the preservation of cultural heritage and cultural values in the territories affected by the destruction of the Kakhovka HPP.
In the future, if necessary, temporary mobile groups may be formed to take measures to protect and preserve cultural heritage sites and cultural property in the combat zone. They should include experts in the field of cultural studies, archeology, architecture, museums, art, etc., as well as the military.
At the same time, it is important to understand that the Armed Forces of Ukraine can be involved in state measures to protect cultural heritage and cultural property not only during martial law, but also in peacetime to overcome the negative consequences of the armed conflict in the relevant area, and to eliminate the consequences of possible natural and man-made emergencies (if they occur). This approach is mobile and makes it possible to create a personnel reserve that will involve military, military-civilian and civilian components in the field of preservation and protection of cultural heritage and cultural property. Thus, the sooner the Ukrainian model is implemented, the more chances we will have to preserve our cultural monuments.
Read this article in Ukrainian and russian.
Please select it with the mouse and press Ctrl+Enter or Submit a bug












 Login with Google
Login with Google